The Ultimate Shed Hunting Guide: Expert Tactics to Find More Deer Antlers
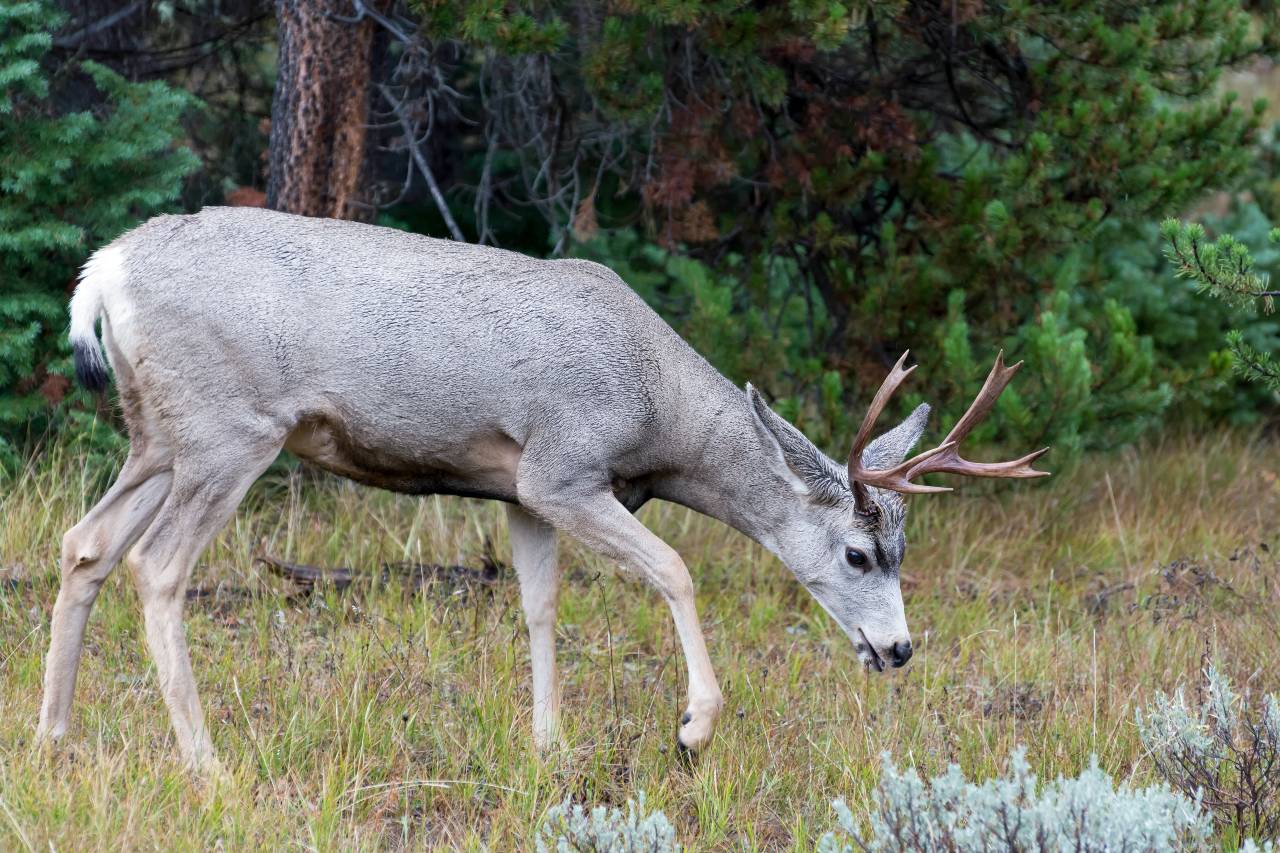

Shed hunting—searching for naturally shed deer antlers—is a rewarding off-season pursuit for hunters, wildlife enthusiasts, and outdoor adventurers alike. Beyond the thrill of discovery, it offers insights into deer behavior, aids in scouting for the upcoming hunting season, and provides a unique way to connect with nature. This comprehensive guide compiles expert strategies, regional insights, and practical tips to enhance your shed hunting success.
Understanding the Antler Shedding Cycle
Why Do Deer Shed Their Antlers?
Male deer, including whitetails and mule deer, shed their antlers annually due to a drop in testosterone levels following the rut (mating season). This hormonal change weakens the tissue at the base of the antlers, causing them to fall off. Shedding allows deer to conserve energy during winter and prepare for new antler growth in the spring.
When Do Deer Shed Their Antlers?
The timing of antler shedding varies based on factors like species, age, health, and environmental conditions:
- Whitetail Deer: Typically shed between late December and early April.
- Mule Deer: Generally shed from mid-February to mid-March.
Older or stressed bucks may shed earlier, while younger, healthier bucks might retain their antlers longer. Monitoring local deer populations through trail cameras can help determine the optimal time to begin shed hunting in your area.
Prime Locations for Shed Hunting
Identifying key areas where deer spend time during winter increases your chances of finding sheds:
1. Bedding Areas
Deer seek sheltered spots to rest, often choosing south-facing slopes that receive ample sunlight. Look for areas with dense cover, such as thickets, conifer stands, or tall grasses.
2. Feeding Areas
Food sources like agricultural fields, food plots, and oak ridges attract deer during winter. Search the perimeters and nearby trails leading to these feeding sites.
3. Travel Corridors
Deer frequently use the same paths between bedding and feeding areas. Focus on well-worn trails, especially where they intersect with obstacles like fences, creeks, or logs—spots where antlers are more likely to be jarred loose.
4. Obstacles and Barriers
Physical features that require deer to jump or duck can cause antlers to dislodge. Inspect fence crossings, stream banks, and low-hanging branches along travel routes.
Essential Gear for Shed Hunting
Equipping yourself with the right tools enhances both safety and success:
- Binoculars: Aid in scanning open fields and distant areas without disturbing wildlife.
- GPS or Mapping Apps: Tools like onX Hunt help track your path and mark locations of found sheds.
- Durable Backpack: Carries essentials like water, snacks, extra clothing, and collected antlers.
- Protective Clothing: Wear weather-appropriate attire and sturdy boots to navigate various terrains comfortably.
- Gloves: Protect hands from thorns, cold, and while handling antlers.
Utilizing Shed Hunting Dogs
Trained dogs can significantly increase shed hunting efficiency. Breeds like Labrador Retrievers, German Shorthaired Pointers, and Bloodhounds possess strong scenting abilities ideal for locating antlers.
Training Tips:
- Introduce Antler Scent: Use real or synthetic antler scents during training sessions.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward dogs with treats or play when they successfully find antlers.
- Consistent Practice: Regular training enhances a dog’s ability to locate sheds in various environments.
Regional Shed Hunting Strategies
Shed hunting tactics can vary based on geographic location:
Northeast & Midwest
- Timing: Prime time is late February through March.
- Focus Areas: South-facing slopes, agricultural fields, and hardwood forests.
Southeast
- Timing: Antler drop may occur later; optimal hunting is in March and early April.
- Focus Areas: Pine thickets, swamp edges, and clear cuts.
Western States
- Timing: Mule deer and elk shed from February to April.
- Focus Areas: Elevated terrains, sagebrush flats, and wintering grounds.
Always check local regulations, as some states have restrictions on shed hunting seasons to protect wildlife during vulnerable periods.
Best Practices and Ethical Considerations
- Respect Wildlife: Avoid disturbing deer during harsh winter conditions; their energy reserves are limited.
- Obtain Permissions: Secure landowner consent before accessing private properties.
- Leave No Trace: Pack out all trash and minimize environmental impact.
- Report Findings: Share data on found sheds with local wildlife agencies if requested; it aids in conservation efforts.
Optimal Timing for Shed Hunting
Timing your shed hunting excursions increases success rates:
- Monitor Deer Activity: Use trail cameras to identify when bucks have shed their antlers.
- Avoid Premature Searches: Entering areas too early can stress deer and cause them to relocate.
- Post-Shed Period: Once the majority have shed, promptly begin searching before rodents and other animals damage or consume the antlers.
Shed hunting blends the excitement of discovery with valuable insights into deer behavior and habitat use. By understanding antler shedding patterns, identifying prime locations, equipping yourself properly, and adhering to ethical practices, you can enhance your shed hunting experiences. Whether you’re a seasoned hunter or a nature enthusiast, the pursuit of shed antlers offers a fulfilling way to engage with the outdoors during the off-season.
- 113
- 3141



